HIGH POWER LED,Side emitting type
Series No:
Weight:(g/pcs)
Dimension:(mm)
Package:
Specification:
Inquiry
Description:
Introduction: Unpacking the Potential of High Power LED Side Emitting Type
High Power LED Side Emitting Types are designed to meet the growing demand for compact, efficient, and versatile lighting solutions. Their unique side-emitting feature allows for creative applications beyond the reach of traditional LEDs, making them a favorite among designers and engineers alike.
Key Features of High Power LED Side Emitting Type
These LEDs are celebrated for their slim profile, high luminous intensity, and unique side-emission of light, making them ideal for edge lighting applications. Additionally, their energy efficiency and long lifespan are highlighted in many “led data sheets,” offering valuable insights into their performance metrics.
Diverse Applications: Lighting the Way with Versatility
The versatility of High Power LED Side Emitting Type is one of its most significant benefits. From creating uniform backlighting for LCD displays to enhancing architectural features and signage, these LEDs provide a solution for challenging lighting designs. Their integration into “led light board circuits” has revolutionized the way light is used in electronics, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Benefits: The Advantages of Going Sideways
Opting for High Power LED Side Emitting Type brings numerous advantages, including enhanced design flexibility, improved energy efficiency, and the ability to create uniform lighting effects in tight spaces. Their low profile and directional output allow for innovative applications in electronics, automotive lighting, and more.
Case Studies: Real-World Impact
Through detailed case studies, this section showcases the transformative effect of High Power LED Side Emitting Type in various industries. From improving safety in automotive applications to enabling sleek and efficient lighting solutions in consumer electronics, these real-world examples underscore the technology’s versatility and effectiveness.
User Testimonials: Voices from the Industry
Testimonials from professionals who have implemented these high-power LEDs in their projects offer firsthand insights into their benefits. Feedback often highlights the improved performance, energy savings, and creative possibilities enabled by “1w leds,” reinforcing the value these components bring to the electronics industry.
Conclusion: Illuminating the Future with High Power LED Side Emitting Type
The exploration of High Power LED Side Emitting Type reveals a technology at the forefront of lighting innovation. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of these LEDs in enabling advanced, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing lighting solutions becomes increasingly clear.
Call to Action
For electronics professionals looking to push the boundaries of lighting design and efficiency, integrating High Power LED Side Emitting Type into your projects is a step toward the future. Explore the potential of “1w leds” and illuminate your designs with unparalleled brilliance and innovation.

Features
- Side Emitting Design: These LEDs emit light from the side of the diode rather than the top, making them ideal for edge lighting and applications where directional light is needed.
- Power Variants – 1W, 3W, and 5W: The range of power options allows for flexibility in lighting intensity and application, catering to both subtle and more pronounced lighting needs.
- Long Service Life: Offering up to 50,000 hours of operation, these LEDs are built for durability and long-term use, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Low Luminosity Loss: Engineered to maintain brightness over time, ensuring consistent light output throughout their lifespan.
- Variety of Emitting Colors: Available in multiple colors to cater to different design requirements and aesthetic preferences.
- Working Current Ranges: Compatible with various power setups, including current ranges of 200-350mA for lower wattage models and up to 700mA and 1050mA for higher wattage models.
- Heat Sink Options: Can come with or without a heat sink. Using a heat sink is beneficial for managing heat dissipation in high-power LEDs, crucial for maintaining performance and extending lifespan.
- RoHS Compliance: Adheres to the Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive, indicating environmentally safe and non-hazardous manufacturing.
Applications
- Edge Lighting: Ideal for applications like acrylic signs, light shelves, and display cases where edge illumination is desired.
- Architectural Lighting: Suitable for creating striking effects in architectural features, cove lighting, and accent lighting in buildings.
- Decorative Lighting: Employed in decorative installations for events, art installations, and commercial spaces.
- Backlighting: Useful for backlighting panels, translucent materials, and creating ambient lighting effects.
- Automotive Lighting: Applied in car interiors and exteriors for aesthetic and functional lighting.
- Signage and Wayfinding: Used in signage, billboards, and wayfinding systems for clear and visible lighting.
- Furniture and Interior Design: Integrated into furniture, shelving, and interior design elements for a modern and stylish look.
- Specialty and Custom Lighting Projects: Popular in custom lighting solutions and DIY projects for their unique lighting characteristics and versatility.


Electrical-optical characteristics:
Package configuration & Internal circuit diagram
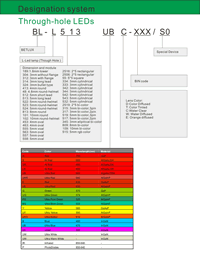
Partno description:
More Information
Lens Color:
| Code | D | T | C | W | E | |
| Meaning | color Diffused | Color Tinted | Water Clear | Water Diffused | Orange diffused |
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta=25°C)
| Parameter | SR | LR | UR | UE | UY | UG | PG | BG | B | UB | UV | W | Unit |
| Forward Current I F | 25 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | mA |
| Power Dissipation P d | 60 | 60 | 60 | 65 | 65 | 75 | 110 | 110 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | mW |
| Reverse Voltage V R | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | V |
| Peak Forward Current I PF (Duty 1/10 @1KHZ) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | mA |
| Operation Temperature T OPR | -40 to +80 | °C | |||||||||||
| Storage Temperature T STG | -40 to +85 | °C | |||||||||||
| Lead Soldering Temperature T SOL | Max.260+-5°C for 3 sec Max. (1.6mm from the base of the epoxy bulb) | °C | |||||||||||
Related Information
Applied for:




The LEDs described here are intended to be used for ordinary electronic equipment (such as office equipment,
communication equipment and household applications). Consult Betlux’s Sales in advance for information on
applications in which exceptional reliability is required, particularly when the failure or malfunction of the LEDs
may directly jeopardize life or health (such as in aviation, transportation, traffic control equipment, medical
and life support systems and safety devices).
CAUTIONS for Through-Hole LED Lamps
1. Application
The LEDs described here are intended to be used for ordinary electronic equipment (such as office equipment, communication equipment and household applications). Consult Betlux’s Sales in advance for information on applications in which exceptional reliability is required, particularly when the failure or malfunction of the LEDs may directly jeopardize life or health (such as in aviation, transportation, traffic control equipment, medical and life support systems and safety devices).
2. Storage
The storage ambient for the LEDs should not exceed 30℃ temperature or 70% relative humidity. It is
recommended that LEDs out of their original packaging are used within three months
For extended storage out of their original packaging, it is recommended that the LEDs be stored in a sealed
container with appropriate desiccant or in a desiccator with nitrogen ambient.
3. Cleaning
Use alcohol-based cleaning solvents such as isopropyl alcohol to clean the LED if necessary
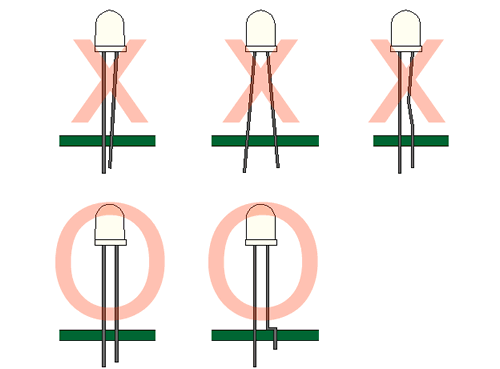
4. Lead Forming & Assembly
During lead forming, the leads should be bent at a point at least 3mm from the base of LED lens. Do not use
the base of the leadframe as a fulcrum during forming.
Lead forming must be done before soldering, at normal temperature.
During assembly on PCB, use minimum clinch force possible to avoid excessive mechanical stress.
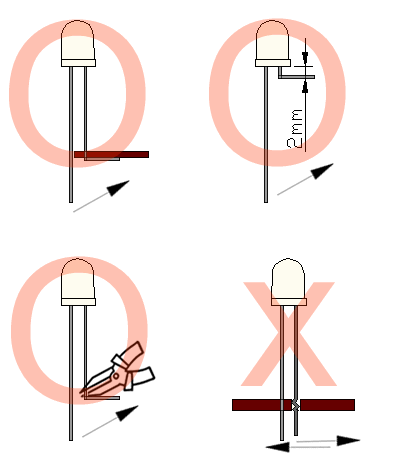
Soldering
When soldering, leave a minimum of 2mm clearance from the base of the base of the lens to the soldering point. Dipping the lens into the solder must be avoided.
Do not apply any external stress to the lead frame during soldering while the LED is at high temperature.
Recommended soldering conditions:
| IR Reflow Soldering (for SMD display) | Wave Soldering | Soldering Iron | |||
| Pre-Heat | 150-180°C | Pre-Heat | 100°C Max. | Temperature | 300°C Max. |
| Pre-Heat Time | 120sec Max. | Pre-Heat Time | 60sec Max. | ||
| Peak Temperature | 260°C Max. | SolderWave | 260°C Max. | Soldering Time | 3sec Max.(one time only) |
| Soldering Time | 10 sec Max. | Soldering Time | 5sec Max. | ||
Note: Excessive soldering temperature and/or time might result in deformation of the LED lens or failure of the LED
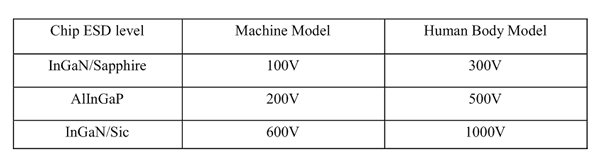
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge)
Static Electricity or power surge will damage the LED.
Suggestions to prevent ESD (Electrostatic Discharge):
n Use a conductive wrist band or anti-electrostatic glove when handling these LEDs
n All devices, equipment, and machinery must be properly grounded
n Work tables, storage racks, etc. should be properly grounded
n Use ion blower to neutralize the static charge which might have built up on surface of the LED’s
plastic lens as a result of friction between LEDs during storage and handling
ESD-damaged LEDs will exhibit abnormal characteristics such as high reverse leakage current,
low forward voltage, or “no light on” at low currents. To verify for ESD damage, check for “light on”
and Vf of the suspect LEDs at low currents.
The Vf of “good” LEDs should be>2.0V@0.1mA for InGaN product and >1.4V@0.1mA for AlInGaP
product.
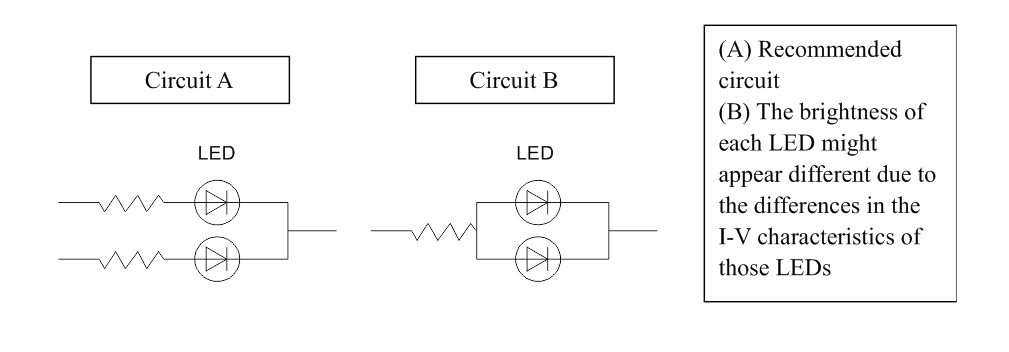
Drive Method
An LED is a current-operated device. In order to ensure intensity uniformity on multiple LEDs connected in
parallel in an application, it is recommended that a current limiting resistor be incorporated in the drive circuit,
in series with each LED as shown in Circuit A below.
When selecting power for LED systems, it’s essential to understand several key parameters to ensure safe operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are some steps and considerations for LED power selection:
- Determine the Forward Voltage (Vf) of the LED(s):
Each LED has a forward voltage, which is the voltage at which the LED operates when the current is flowing through it. This value can typically be found in the LED’s datasheet.
- Determine the Forward Current (If) of the LED(s):
The forward current is the current at which the LED is designed to operate. Running an LED at higher than its rated current can reduce its lifespan and increase the heat it produces.
- Decide on the Configuration:
Series Configuration: When LEDs are connected in series, the forward voltages add up, but the current remains the same.
Parallel Configuration: When LEDs are connected in parallel, the forward voltage remains the same, but the currents add up. This configuration can be risky because if one LED fails or has a slightly lower forward voltage, it can cause the other LEDs to draw more current.
Calculate Total Power Requirements:
Power (W) = Total Forward Voltage (V) x Total Forward Current (A)
For example, if you have three LEDs connected in series, each with a forward voltage of 3V and a forward current of 20mA, the total power requirement would be:
Power = (3V + 3V + 3V) x 20mA = 9V x 0.02A = 0.18W
- Select an Appropriate Power Supply:
- Voltage Rating: The power supply voltage should match or slightly exceed the total forward voltage of your LED configuration.
- Current Rating: The power supply’s current rating should meet or exceed the total forward current of your LED configuration.
- Safety Margin: It’s a good practice to select a power supply that can provide at least 20% more power than your calculated requirement. This ensures the power supply isn’t operating at its maximum capacity, which can extend its life and ensure safer operation.
- Consider Additional Features:
- Dimming Capability: If you want to control the brightness of your LEDs, choose a power supply with dimming capabilities.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: To protect your LEDs, select a power supply with built-in protection mechanisms.
- Thermal Management: Ensure that the power supply has adequate cooling, especially if it will be enclosed or in a location with limited airflow.
- Regulation and Efficiency:A power supply with good regulation will maintain a consistent voltage output despite variations in the load. High efficiency ensures minimal power is wasted as heat.
- Physical Size and Form Factor:Depending on where you plan to place the power supply, its size and shape may be critical factors.
In summary, when selecting power for LED systems, understanding your LED’s requirements and the configuration you plan to use is essential. Then, pick a power supply that meets those needs with some added safety margin, keeping in mind any additional features or constraints relevant to your project.
Here are some well-regarded brands in the industry:
- Mean Well: One of the most recognized brands in the LED power supply industry, Mean Well offers a wide range of products suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their units often come with features like overcurrent protection, dimming capabilities, and high efficiency.
- Tridonic: A global leader in lighting technology, Tridonic offers LED drivers and power supplies that cater to various lighting solutions, from simple setups to advanced smart lighting systems.
- Philips Advance Xitanium: Philips is a well-known brand in the lighting industry, and their Xitanium series of LED drivers are known for reliability and performance. They cater to both indoor and outdoor LED applications.
- Osram: Another giant in the lighting industry, Osram offers a range of LED drivers and power supplies suitable for various applications, including architectural and street lighting.
- LIFUD: Specializing in LED drivers, LIFUD is known for its high-quality products that cater to both commercial and residential LED lighting solutions.
- MOSO: This brand offers a variety of LED drivers, especially for outdoor and industrial applications. Their products are known for durability and performance.
- TDK-Lambda: With a history in power electronics, TDK-Lambda offers a range of power supplies and LED drivers suitable for various applications, emphasizing reliability and advanced features.