3mm LED diode | Ultra Green
Article No:
Color:
Weight:(g/pcs)
Dimension:(mm)
Inquiry
Related Article List
Article No | color | material | wavelength | apperance | v_typ | v_max | luminous_min | luminous_typ | degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Orange |
GaAsP/GaP |
635 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
5 |
15 |
100 |
||
Green |
GaP/GaP |
570 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
3 |
10 |
100 |
||
Ultra Green |
AlGaInP |
574 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
70 |
120 |
100 |
||
Ultra orange |
AlGaInP |
630 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
90 |
180 |
100 |
||
Yellow |
GaAsP/GaP |
585 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
3 |
10 |
100 |
||
Green |
GaP/GaP |
570 |
Water Diff. |
2.5 |
3 |
10 |
100 |
Product Series information
Product Series |
|---|
 Series No:BL-L345 Dimension 3 × 3.8 × 6.1 mm Description: ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Illuminating Innovation: The Two-Color 3mm LED DiodeAt the forefront of LED technology lies the two-color 3mm LED diode, a marvel of engineering that combines two distinct colors in a single package. This compact component, known for its efficiency and versatility, is capable of emitting different colors without the need for multiple LEDs. This ability not only saves space but also opens up a realm of creative possibilities for electronic device design.Distinct Features of Two-Color 3mm LEDs
Diverse Applications: From Indicators to AmbianceThe applications of two-color 3mm LED diodes are vast and varied. They are commonly used as status indicators on electronic devices, where they can signal different modes or alerts through color changes. Additionally, these LEDs are perfect for creating ambient lighting in consumer electronics, offering a range of colors to enhance the user experience. Beyond these, multi-color LEDs find applications in signage, automotive lighting, and decorative installations, where their compact size and dual-color capabilities provide unmatched versatility.Benefits of Integrating Two-Color 3mm LEDsChoosing two-color 3mm LED diodes for electronic projects offers several advantages:
Case Studies: Lighting the Way ForwardOne compelling case study involves a leading consumer electronics brand that utilized two-color 3mm LEDs in their latest line of smart home devices. The LEDs served as dynamic indicators for device status, such as power on/off and connectivity status, significantly enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the products.User Testimonials: Shining a Light on Success"We've seen remarkable improvements in product design and user feedback since incorporating two-color 3mm LEDs into our devices," states a Product Development Engineer from a renowned tech company. "Their versatility and efficiency have allowed us to innovate beyond traditional constraints."Conclusion: The Bright Future of Two-Color 3mm LEDsThe exploration into the world of two-color 3mm LED diodes reveals their critical role in advancing the design and functionality of modern electronics. With their unique blend of compactness, efficiency, and dual-color capabilities, these LEDs are set to remain at the forefront of electronic component innovation. As technology continues to evolve, the significance of incorporating efficient, versatile components like the two-color 3mm LED diode becomes increasingly apparent. Call to Action: Step into the future of electronics with the innovative two-color 3mm LED diode. Discover how these compact, versatile components can transform your projects, offering enhanced functionality and design aesthetics. Embrace the power of dual-color illumination and elevate your electronic designs to new heights. Features
Applications
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Dimension and Circuit Drawing: 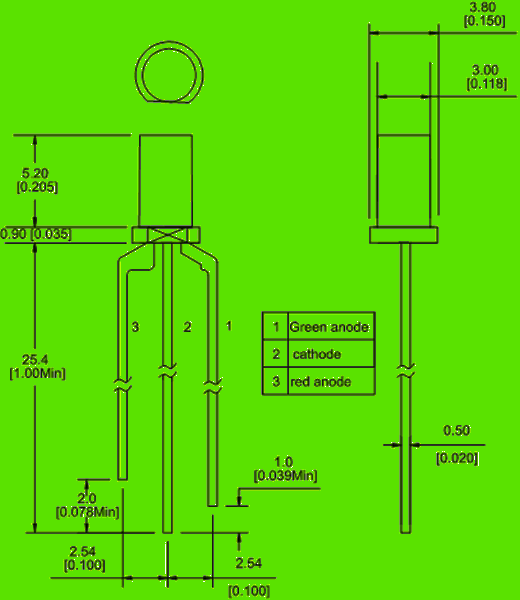 |
Related Information
Soldering
When soldering, leave a minimum of 2mm clearance from the base of the base of the lens to the soldering point. Dipping the lens into the solder must be avoided.
Do not apply any external stress to the lead frame during soldering while the LED is at high temperature.
Recommended soldering conditions:
| IR Reflow Soldering (for SMD display) | Wave Soldering | Soldering Iron | |||
| Pre-Heat | 150-180°C | Pre-Heat | 100°C Max. | Temperature | 300°C Max. |
| Pre-Heat Time | 120sec Max. | Pre-Heat Time | 60sec Max. | ||
| Peak Temperature | 260°C Max. | SolderWave | 260°C Max. | Soldering Time | 3sec Max.(one time only) |
| Soldering Time | 10 sec Max. | Soldering Time | 5sec Max. | ||
Note: Excessive soldering temperature and/or time might result in deformation of the LED lens or failure of the LED
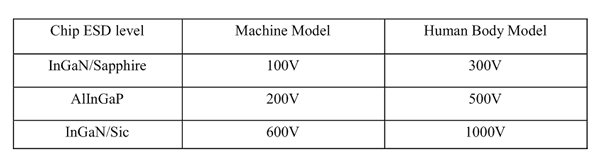
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge)
Static Electricity or power surge will damage the LED.
Suggestions to prevent ESD (Electrostatic Discharge):
n Use a conductive wrist band or anti-electrostatic glove when handling these LEDs
n All devices, equipment, and machinery must be properly grounded
n Work tables, storage racks, etc. should be properly grounded
n Use ion blower to neutralize the static charge which might have built up on surface of the LED’s
plastic lens as a result of friction between LEDs during storage and handling
ESD-damaged LEDs will exhibit abnormal characteristics such as high reverse leakage current,
low forward voltage, or “no light on” at low currents. To verify for ESD damage, check for “light on”
and Vf of the suspect LEDs at low currents.
The Vf of “good” LEDs should be>2.0V@0.1mA for InGaN product and >1.4V@0.1mA for AlInGaP
product.
When selecting power for LED systems, it’s essential to understand several key parameters to ensure safe operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are some steps and considerations for LED power selection:
- Determine the Forward Voltage (Vf) of the LED(s):
Each LED has a forward voltage, which is the voltage at which the LED operates when the current is flowing through it. This value can typically be found in the LED’s datasheet.
- Determine the Forward Current (If) of the LED(s):
The forward current is the current at which the LED is designed to operate. Running an LED at higher than its rated current can reduce its lifespan and increase the heat it produces.
- Decide on the Configuration:
Series Configuration: When LEDs are connected in series, the forward voltages add up, but the current remains the same.
Parallel Configuration: When LEDs are connected in parallel, the forward voltage remains the same, but the currents add up. This configuration can be risky because if one LED fails or has a slightly lower forward voltage, it can cause the other LEDs to draw more current.
Calculate Total Power Requirements:
Power (W) = Total Forward Voltage (V) x Total Forward Current (A)
For example, if you have three LEDs connected in series, each with a forward voltage of 3V and a forward current of 20mA, the total power requirement would be:
Power = (3V + 3V + 3V) x 20mA = 9V x 0.02A = 0.18W
- Select an Appropriate Power Supply:
- Voltage Rating: The power supply voltage should match or slightly exceed the total forward voltage of your LED configuration.
- Current Rating: The power supply’s current rating should meet or exceed the total forward current of your LED configuration.
- Safety Margin: It’s a good practice to select a power supply that can provide at least 20% more power than your calculated requirement. This ensures the power supply isn’t operating at its maximum capacity, which can extend its life and ensure safer operation.
- Consider Additional Features:
- Dimming Capability: If you want to control the brightness of your LEDs, choose a power supply with dimming capabilities.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: To protect your LEDs, select a power supply with built-in protection mechanisms.
- Thermal Management: Ensure that the power supply has adequate cooling, especially if it will be enclosed or in a location with limited airflow.
- Regulation and Efficiency:A power supply with good regulation will maintain a consistent voltage output despite variations in the load. High efficiency ensures minimal power is wasted as heat.
- Physical Size and Form Factor:Depending on where you plan to place the power supply, its size and shape may be critical factors.
In summary, when selecting power for LED systems, understanding your LED’s requirements and the configuration you plan to use is essential. Then, pick a power supply that meets those needs with some added safety margin, keeping in mind any additional features or constraints relevant to your project.
Here are some well-regarded brands in the industry:
- Mean Well: One of the most recognized brands in the LED power supply industry, Mean Well offers a wide range of products suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their units often come with features like overcurrent protection, dimming capabilities, and high efficiency.
- Tridonic: A global leader in lighting technology, Tridonic offers LED drivers and power supplies that cater to various lighting solutions, from simple setups to advanced smart lighting systems.
- Philips Advance Xitanium: Philips is a well-known brand in the lighting industry, and their Xitanium series of LED drivers are known for reliability and performance. They cater to both indoor and outdoor LED applications.
- Osram: Another giant in the lighting industry, Osram offers a range of LED drivers and power supplies suitable for various applications, including architectural and street lighting.
- LIFUD: Specializing in LED drivers, LIFUD is known for its high-quality products that cater to both commercial and residential LED lighting solutions.
- MOSO: This brand offers a variety of LED drivers, especially for outdoor and industrial applications. Their products are known for durability and performance.
- TDK-Lambda: With a history in power electronics, TDK-Lambda offers a range of power supplies and LED drivers suitable for various applications, emphasizing reliability and advanced features.



