Phototransistors LED,Miniature Device LED,1.8 mm Round Tower
Article No:
Color:
Weight:(g/pcs)
Dimension:(mm)
Inquiry
Product Series information
Product Series |
|---|
 Series No:BL-LM18GPT Dimension 7.9 × 9.15 × 11 mm Description: ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ "Compact Powerhouses: The Emergence of Phototransistors in 1.8 mm LED Technology"
In the dynamic field of electronics, the integration of phototransistors with miniature LEDs, especially those in the 1.8 mm round tower format, represents a significant advancement. This combination is not just a feat of miniaturization but also an innovation in optical sensing technology. Aimed at a discerning audience of engineers, purchasers, and administrators in the USA and UK, this article will explore the unique features, applications, and benefits of phototransistor LED technology, supplemented by compelling case studies and user testimonials.
Understanding Phototransistors and Their Integration with LEDs
Phototransistors are semiconductor devices that convert light into an electrical signal, functioning similarly to traditional transistors but with light as the primary input instead of electric current. When integrated with LEDs, particularly in a miniature format like the 1.8 mm round tower, they offer enhanced sensitivity and precision in detecting light. This synergy between phototransistors and LEDs paves the way for innovative applications in various sectors.
Features and Technological Advancements
The fusion of phototransistors with 1.8 mm LEDs has led to the creation of devices that are not only compact but also highly efficient. These miniature LEDs offer the dual benefits of small size and high performance, making them suitable for space-constrained applications where precision is paramount. The combination of phototransistors with these LEDs results in devices that can quickly and accurately respond to light changes, making them ideal for a range of sensing applications.
Diverse Applications in Modern Technology
Phototransistor LEDs, especially in the 1.8 mm size, find applications across a spectrum of industries. In consumer electronics, they are used for touchless switches and light-dependent controls. In industrial settings, these devices are integral to optical sensors that monitor processes and ensure safety. The automotive sector utilizes them in systems like automatic headlights and dashboard illumination controls.
Benefits and Advantages
The primary advantage of integrating phototransistors with miniature LEDs lies in their efficiency and compactness. They provide precise light sensing capabilities while occupying minimal space, a critical factor in modern electronic device design. Additionally, their low power consumption and long lifespan make them an environmentally friendly and cost-effective choice for both manufacturers and consumers.
Case Studies: Real-World Impact
A case study involving a leading smartphone manufacturer demonstrated the utility of these devices. The company incorporated 1.8 mm phototransistor LEDs into their latest smartphone model for an adaptive brightness feature, significantly enhancing user experience while conserving battery life.
Another example comes from the automotive industry. A car manufacturer integrated these phototransistor LEDs into their new model's headlight system, improving safety by automatically adjusting headlight brightness in response to external light conditions.
User Testimonials
Testimonials from professionals in the electronics field further underscore the impact of these devices. An electronics engineer from a major tech company praised the precision and compactness of the 1.8 mm phototransistor LEDs, noting their crucial role in developing their latest wearable technology. A procurement officer highlighted the cost-efficiency and reliability of these components, which have become a standard in their product line.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Phototransistor LEDs, particularly in the 1.8 mm round tower format, are redefining the boundaries of electronic component design. For professionals in the electronics industry , leveraging these components is not just an option but a necessity for staying at the forefront of innovation. Embrace these compact powerhouses in your next project to unlock new levels of efficiency and performance.
Features:
1.8mm Round Type photo-transistor
High Reliability
High photo sensitivity
Water Clear, black available
Fast response time
Application
Infrared applied system
Smoke detector
Infrared Camera
Printer
Optoelectronic switch
Infrared applied system ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Dimension and Circuit Drawing:  |
Related Article List
Related Information
Soldering
When soldering, leave a minimum of 2mm clearance from the base of the base of the lens to the soldering point. Dipping the lens into the solder must be avoided.
Do not apply any external stress to the lead frame during soldering while the LED is at high temperature.
Recommended soldering conditions:
| IR Reflow Soldering (for SMD display) | Wave Soldering | Soldering Iron | |||
| Pre-Heat | 150-180°C | Pre-Heat | 100°C Max. | Temperature | 300°C Max. |
| Pre-Heat Time | 120sec Max. | Pre-Heat Time | 60sec Max. | ||
| Peak Temperature | 260°C Max. | SolderWave | 260°C Max. | Soldering Time | 3sec Max.(one time only) |
| Soldering Time | 10 sec Max. | Soldering Time | 5sec Max. | ||
Note: Excessive soldering temperature and/or time might result in deformation of the LED lens or failure of the LED
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge)
Static Electricity or power surge will damage the LED.
Suggestions to prevent ESD (Electrostatic Discharge):
n Use a conductive wrist band or anti-electrostatic glove when handling these LEDs
n All devices, equipment, and machinery must be properly grounded
n Work tables, storage racks, etc. should be properly grounded
n Use ion blower to neutralize the static charge which might have built up on surface of the LED’s
plastic lens as a result of friction between LEDs during storage and handling
ESD-damaged LEDs will exhibit abnormal characteristics such as high reverse leakage current,
low forward voltage, or “no light on” at low currents. To verify for ESD damage, check for “light on”
and Vf of the suspect LEDs at low currents.
The Vf of “good” LEDs should be>2.0V@0.1mA for InGaN product and >1.4V@0.1mA for AlInGaP
product.
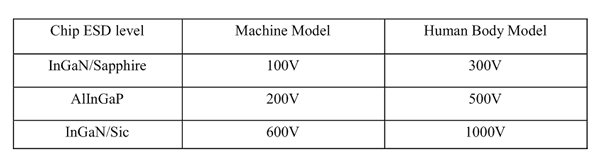
When selecting power for LED systems, it’s essential to understand several key parameters to ensure safe operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are some steps and considerations for LED power selection:
- Determine the Forward Voltage (Vf) of the LED(s):
Each LED has a forward voltage, which is the voltage at which the LED operates when the current is flowing through it. This value can typically be found in the LED’s datasheet.
- Determine the Forward Current (If) of the LED(s):
The forward current is the current at which the LED is designed to operate. Running an LED at higher than its rated current can reduce its lifespan and increase the heat it produces.
- Decide on the Configuration:
Series Configuration: When LEDs are connected in series, the forward voltages add up, but the current remains the same.
Parallel Configuration: When LEDs are connected in parallel, the forward voltage remains the same, but the currents add up. This configuration can be risky because if one LED fails or has a slightly lower forward voltage, it can cause the other LEDs to draw more current.
Calculate Total Power Requirements:
Power (W) = Total Forward Voltage (V) x Total Forward Current (A)
For example, if you have three LEDs connected in series, each with a forward voltage of 3V and a forward current of 20mA, the total power requirement would be:
Power = (3V + 3V + 3V) x 20mA = 9V x 0.02A = 0.18W
- Select an Appropriate Power Supply:
- Voltage Rating: The power supply voltage should match or slightly exceed the total forward voltage of your LED configuration.
- Current Rating: The power supply’s current rating should meet or exceed the total forward current of your LED configuration.
- Safety Margin: It’s a good practice to select a power supply that can provide at least 20% more power than your calculated requirement. This ensures the power supply isn’t operating at its maximum capacity, which can extend its life and ensure safer operation.
- Consider Additional Features:
- Dimming Capability: If you want to control the brightness of your LEDs, choose a power supply with dimming capabilities.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: To protect your LEDs, select a power supply with built-in protection mechanisms.
- Thermal Management: Ensure that the power supply has adequate cooling, especially if it will be enclosed or in a location with limited airflow.
- Regulation and Efficiency:A power supply with good regulation will maintain a consistent voltage output despite variations in the load. High efficiency ensures minimal power is wasted as heat.
- Physical Size and Form Factor:Depending on where you plan to place the power supply, its size and shape may be critical factors.
In summary, when selecting power for LED systems, understanding your LED’s requirements and the configuration you plan to use is essential. Then, pick a power supply that meets those needs with some added safety margin, keeping in mind any additional features or constraints relevant to your project.
Here are some well-regarded brands in the industry:
- Mean Well: One of the most recognized brands in the LED power supply industry, Mean Well offers a wide range of products suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their units often come with features like overcurrent protection, dimming capabilities, and high efficiency.
- Tridonic: A global leader in lighting technology, Tridonic offers LED drivers and power supplies that cater to various lighting solutions, from simple setups to advanced smart lighting systems.
- Philips Advance Xitanium: Philips is a well-known brand in the lighting industry, and their Xitanium series of LED drivers are known for reliability and performance. They cater to both indoor and outdoor LED applications.
- Osram: Another giant in the lighting industry, Osram offers a range of LED drivers and power supplies suitable for various applications, including architectural and street lighting.
- LIFUD: Specializing in LED drivers, LIFUD is known for its high-quality products that cater to both commercial and residential LED lighting solutions.
- MOSO: This brand offers a variety of LED drivers, especially for outdoor and industrial applications. Their products are known for durability and performance.
- TDK-Lambda: With a history in power electronics, TDK-Lambda offers a range of power supplies and LED drivers suitable for various applications, emphasizing reliability and advanced features.



