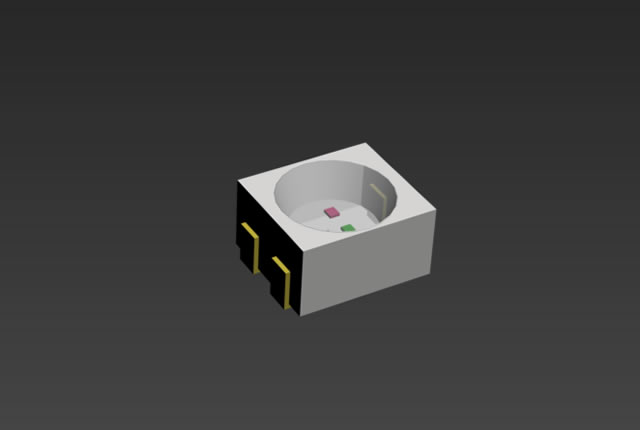
3528 SMD led diode, RGB color
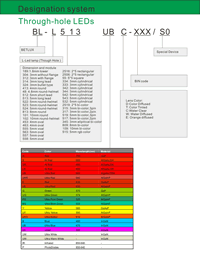
Series No:
Weight:(g/pcs)
Dimension:(mm)
Package:
Specification:
Inquiry
Description:
Unleashing Color: The Power of 3528 SMD RGB LED Diodes in Modern Electronics
In the evolving world of electronics, RGB LEDs have become a cornerstone for creating vibrant, colorful displays and lighting solutions. The 3528 SMD LED diode, particularly in its RGB configuration, stands out due to its versatility and efficiency. Known for their compact size and bright output, these RGB LED SMDs offer a dynamic color range that is essential in various applications. This comprehensive article explores the significant features, applications, and benefits of 3528 SMD RGB LED diodes, enriched with user testimonials and case studies.
Innovative Features of the 3528 SMD RGB LED
The 3528 SMD RGB LED, often compared to the slightly larger 2835 LED for its application in surface-mount technology, integrates red, green, and blue diodes in one package. This integration allows it to produce a spectrum of colors through color mixing, providing countless possibilities for customization and creativity in lighting designs. These LEDs are designed to offer not only a wide color range but also high efficiency and durability, making them suitable for both commercial and residential applications.
Versatile Applications of RGB LED SMDs
3528 RGB LEDs are utilized across a broad array of industries:
- Consumer Electronics: From smartphones to TVs, these LEDs backlight screens and buttons, enhancing user interfaces with vivid colors.
- Architectural Lighting: They light up buildings, bridges, and landmarks, offering dramatic lighting effects that can change in response to events or environmental conditions.
- Automotive: Used in dashboard lighting, accent lights, and tail lights, they improve aesthetic appeal and functionality in vehicles.
The Benefits of Using 3528 SMD RGB LEDs
Employing 3528 SMD RGB LEDs in electronic and lighting projects offers significant advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: These LEDs consume less power compared to traditional lighting solutions, leading to lower energy costs.
- Compact Design: The small footprint of the 3528 LED allows for its use in space-constrained applications without sacrificing brightness or color quality.
- Longevity: With a longer lifespan than many other lighting options, these LEDs reduce the need for frequent replacements, thereby decreasing maintenance costs.
Case Studies: Demonstrating Success with 3528 RGB LEDs
One compelling case study involves a major city’s use of 3528 SMD RGB LEDs in a landmark bridge lighting project. The project involved installing thousands of these LEDs to create an interactive light display that responds to traffic and weather conditions, significantly enhancing the city’s night-time aesthetics and attracting tourists.
User Testimonials: Insights from Professionals
Feedback from electronics manufacturers and lighting designers who have utilized 3528 SMD RGB LEDs consistently highlights the positive impact of these components. A chief technology officer in a leading electronics firm noted, “The 3528 RGB LEDs have allowed us to push the boundaries of product design, enabling not only functionality but also incredible visual appeal.”
Advancing Technology with UV ABC Innovations
While primarily known for visible light applications, advancements in LED technology have extended the use of SMD LEDs like the 3528 into the ultraviolet spectrum, categorized as UV ABC. These developments open new doors for using 3528 LEDs in medical, sterilization, and authentication applications, where specific UV wavelengths are required.
Conclusion: Why Choose 3528 SMD RGB LEDs for Your Next Project?
As technology continues to advance, the 3528 SMD RGB LED remains at the forefront, driving innovations in color lighting solutions. For engineers, designers, and administrators in the electronics and lighting industries, these LEDs offer an optimal blend of functionality, creativity, and efficiency. Whether for enhancing product designs, creating atmospheric lighting solutions, or innovating with new applications, 3528 SMD RGB LEDs provide the tools necessary for success.

Features: 3528 SMD LED Diode, RGB Color
- Compact size: 3.5mm x 2.8mm SMD, 1.9mm thickness, PLCC4 package
- RGB-color type with ultra brightness
- Compatible with automatic placement equipment
- Wide viewing angle for versatile applications
- Ideal for backlighting and indicator purposes
- Package: 2,000 pieces per reel
- RoHS compliant
Applications:
- Backlighting for electronic displays
- Indicator lights in various devices
- Colorful displays in consumer electronics
- Decorative lighting in signage
- Compact and space-sensitive lighting designs


Electrical-optical characteristics:
Package configuration & Internal circuit diagram
Partno description:
More Information
Lens Color:
| Code | D | T | C | W | E | |
| Meaning | color Diffused | Color Tinted | Water Clear | Water Diffused | Orange diffused |
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta=25°C)
| Parameter | SR | LR | UR | UE | UY | UG | PG | BG | B | UB | UV | W | Unit |
| Forward Current I F | 25 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | mA |
| Power Dissipation P d | 60 | 60 | 60 | 65 | 65 | 75 | 110 | 110 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | mW |
| Reverse Voltage V R | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | V |
| Peak Forward Current I PF (Duty 1/10 @1KHZ) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | mA |
| Operation Temperature T OPR | -40 to +80 | °C | |||||||||||
| Storage Temperature T STG | -40 to +85 | °C | |||||||||||
| Lead Soldering Temperature T SOL | Max.260+-5°C for 3 sec Max. (1.6mm from the base of the epoxy bulb) | °C | |||||||||||
Related Information
Applied for:




The LEDs described here are intended to be used for ordinary electronic equipment (such as office equipment,
communication equipment and household applications). Consult Betlux’s Sales in advance for information on
applications in which exceptional reliability is required, particularly when the failure or malfunction of the LEDs
may directly jeopardize life or health (such as in aviation, transportation, traffic control equipment, medical
and life support systems and safety devices).
CAUTIONS for Through-Hole LED Lamps
1. Application
The LEDs described here are intended to be used for ordinary electronic equipment (such as office equipment, communication equipment and household applications). Consult Betlux’s Sales in advance for information on applications in which exceptional reliability is required, particularly when the failure or malfunction of the LEDs may directly jeopardize life or health (such as in aviation, transportation, traffic control equipment, medical and life support systems and safety devices).
2. Storage
The storage ambient for the LEDs should not exceed 30℃ temperature or 70% relative humidity. It is
recommended that LEDs out of their original packaging are used within three months
For extended storage out of their original packaging, it is recommended that the LEDs be stored in a sealed
container with appropriate desiccant or in a desiccator with nitrogen ambient.
3. Cleaning
Use alcohol-based cleaning solvents such as isopropyl alcohol to clean the LED if necessary
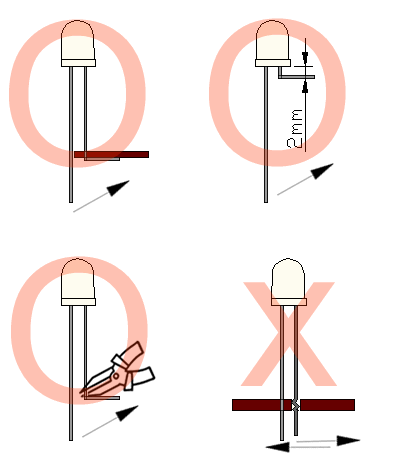
4. Lead Forming & Assembly
During lead forming, the leads should be bent at a point at least 3mm from the base of LED lens. Do not use
the base of the leadframe as a fulcrum during forming.
Lead forming must be done before soldering, at normal temperature.
During assembly on PCB, use minimum clinch force possible to avoid excessive mechanical stress.
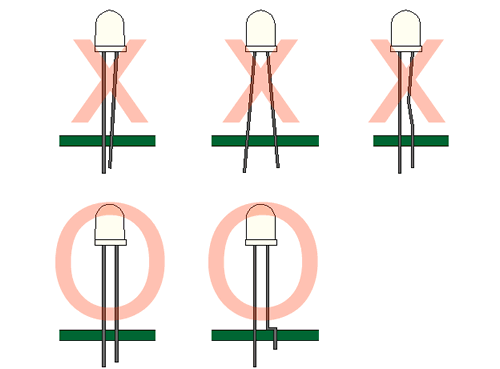
Soldering
When soldering, leave a minimum of 2mm clearance from the base of the base of the lens to the soldering point. Dipping the lens into the solder must be avoided.
Do not apply any external stress to the lead frame during soldering while the LED is at high temperature.
Recommended soldering conditions:
| IR Reflow Soldering (for SMD display) | Wave Soldering | Soldering Iron | |||
| Pre-Heat | 150-180°C | Pre-Heat | 100°C Max. | Temperature | 300°C Max. |
| Pre-Heat Time | 120sec Max. | Pre-Heat Time | 60sec Max. | ||
| Peak Temperature | 260°C Max. | SolderWave | 260°C Max. | Soldering Time | 3sec Max.(one time only) |
| Soldering Time | 10 sec Max. | Soldering Time | 5sec Max. | ||
Note: Excessive soldering temperature and/or time might result in deformation of the LED lens or failure of the LED
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge)
Static Electricity or power surge will damage the LED.
Suggestions to prevent ESD (Electrostatic Discharge):
n Use a conductive wrist band or anti-electrostatic glove when handling these LEDs
n All devices, equipment, and machinery must be properly grounded
n Work tables, storage racks, etc. should be properly grounded
n Use ion blower to neutralize the static charge which might have built up on surface of the LED’s
plastic lens as a result of friction between LEDs during storage and handling
ESD-damaged LEDs will exhibit abnormal characteristics such as high reverse leakage current,
low forward voltage, or “no light on” at low currents. To verify for ESD damage, check for “light on”
and Vf of the suspect LEDs at low currents.
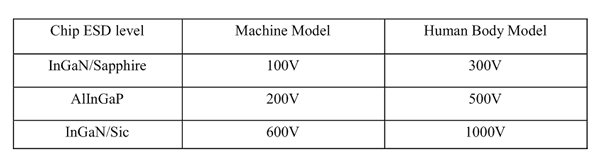
The Vf of “good” LEDs should be>2.0V@0.1mA for InGaN product and >1.4V@0.1mA for AlInGaP
product.
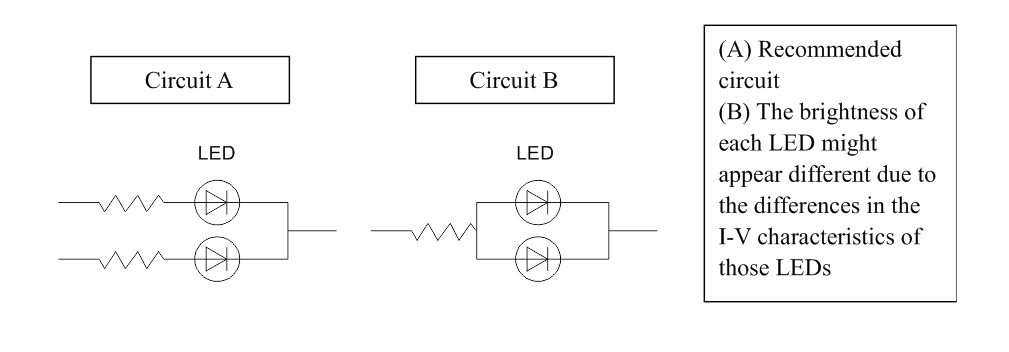
Drive Method
An LED is a current-operated device. In order to ensure intensity uniformity on multiple LEDs connected in
parallel in an application, it is recommended that a current limiting resistor be incorporated in the drive circuit,
in series with each LED as shown in Circuit A below.
When selecting power for LED systems, it’s essential to understand several key parameters to ensure safe operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are some steps and considerations for LED power selection:
- Determine the Forward Voltage (Vf) of the LED(s):
Each LED has a forward voltage, which is the voltage at which the LED operates when the current is flowing through it. This value can typically be found in the LED’s datasheet.
- Determine the Forward Current (If) of the LED(s):
The forward current is the current at which the LED is designed to operate. Running an LED at higher than its rated current can reduce its lifespan and increase the heat it produces.
- Decide on the Configuration:
Series Configuration: When LEDs are connected in series, the forward voltages add up, but the current remains the same.
Parallel Configuration: When LEDs are connected in parallel, the forward voltage remains the same, but the currents add up. This configuration can be risky because if one LED fails or has a slightly lower forward voltage, it can cause the other LEDs to draw more current.
Calculate Total Power Requirements:
Power (W) = Total Forward Voltage (V) x Total Forward Current (A)
For example, if you have three LEDs connected in series, each with a forward voltage of 3V and a forward current of 20mA, the total power requirement would be:
Power = (3V + 3V + 3V) x 20mA = 9V x 0.02A = 0.18W
- Select an Appropriate Power Supply:
- Voltage Rating: The power supply voltage should match or slightly exceed the total forward voltage of your LED configuration.
- Current Rating: The power supply’s current rating should meet or exceed the total forward current of your LED configuration.
- Safety Margin: It’s a good practice to select a power supply that can provide at least 20% more power than your calculated requirement. This ensures the power supply isn’t operating at its maximum capacity, which can extend its life and ensure safer operation.
- Consider Additional Features:
- Dimming Capability: If you want to control the brightness of your LEDs, choose a power supply with dimming capabilities.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: To protect your LEDs, select a power supply with built-in protection mechanisms.
- Thermal Management: Ensure that the power supply has adequate cooling, especially if it will be enclosed or in a location with limited airflow.
- Regulation and Efficiency:A power supply with good regulation will maintain a consistent voltage output despite variations in the load. High efficiency ensures minimal power is wasted as heat.
- Physical Size and Form Factor:Depending on where you plan to place the power supply, its size and shape may be critical factors.
In summary, when selecting power for LED systems, understanding your LED’s requirements and the configuration you plan to use is essential. Then, pick a power supply that meets those needs with some added safety margin, keeping in mind any additional features or constraints relevant to your project.
Here are some well-regarded brands in the industry:
- Mean Well: One of the most recognized brands in the LED power supply industry, Mean Well offers a wide range of products suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their units often come with features like overcurrent protection, dimming capabilities, and high efficiency.
- Tridonic: A global leader in lighting technology, Tridonic offers LED drivers and power supplies that cater to various lighting solutions, from simple setups to advanced smart lighting systems.
- Philips Advance Xitanium: Philips is a well-known brand in the lighting industry, and their Xitanium series of LED drivers are known for reliability and performance. They cater to both indoor and outdoor LED applications.
- Osram: Another giant in the lighting industry, Osram offers a range of LED drivers and power supplies suitable for various applications, including architectural and street lighting.
- LIFUD: Specializing in LED drivers, LIFUD is known for its high-quality products that cater to both commercial and residential LED lighting solutions.
- MOSO: This brand offers a variety of LED drivers, especially for outdoor and industrial applications. Their products are known for durability and performance.
- TDK-Lambda: With a history in power electronics, TDK-Lambda offers a range of power supplies and LED drivers suitable for various applications, emphasizing reliability and advanced features.