0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment led display
Series No:
Weight:(g/pcs)
Dimension:(mm)
Character Height: (inch)
Specification:
Inquiry
Description:
Elevating Digital Readability: The Evolution of 0.56 Inch Dual-Digit Seven Segment LED Displays
The digital era demands precision, efficiency, and clarity in the way information is displayed. Enter the 0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment LED display, a marvel in the realm of digital displays, offering unmatched readability and versatility. This comprehensive article aims to explore the features, applications, and substantial benefits of these displays, enriched with case studies and testimonials from the electronics field. Targeted at electronics manufacturer engineers, purchasers, and administrators, it sheds light on why this technology is pivotal in modern electronics design and manufacturing.
Introduction: The Dual-Digit Seven Segment LED Display
In the forefront of digital display technology, the 2 seven segment display, specifically the 0.56 inch 7 segment model, represents a significant advancement. With its ability to convey information with high visibility and minimal power consumption, it has become a critical component across a wide range of applications.
Features and Versatile Applications
The dual-digit format offers a compact yet effective means of data presentation, ideal for devices where space and power efficiency are crucial. From consumer electronics, such as digital watches and calculators, to more sophisticated uses in medical devices, automotive dashboards, and industrial control panels, the 0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment LED display stands out for its clarity and reliability.
Key Advantages for the Electronics Industry
Incorporating these displays into electronic products brings several advantages. Not only do they enhance the aesthetic appeal and usability of devices, but they also contribute to longer battery life and reduced energy costs thanks to their efficiency. The simplicity of programming these displays allows for quicker development cycles, enabling faster time-to-market for new products.
Case Studies: Transformative Impact
The adoption of 14mm 7 segment display technology has led to remarkable improvements in device functionality and user experience across various sectors. A highlighted case study involves a leading electronics company that integrated the 7 segment board into their latest home appliance line, significantly enhancing interface interaction and overall customer satisfaction.
Professional Insights: User Testimonials
Testimonials from the field underline the 0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment LED display’s reliability and ease of integration, highlighting its pivotal role in the development of innovative and user-centric products. Feedback from engineers and purchasers alike points to its effectiveness in improving product appeal and marketability.
Future Outlook: Advancements and Trends
The 0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment LED display continues to evolve, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing brightness, efficiency, and adaptability. Emerging materials and technologies promise to expand the applications and capabilities of these displays, ensuring their prominence in the next wave of electronic device development.
Conclusion: Adopting Advanced Display Technology
The 0.56 inch dual-digit seven segment LED display is not merely a component but a cornerstone of modern digital display technology. Its widespread adoption underscores its utility, efficiency, and the enhanced user experience it offers. For those in electronics manufacturing, leveraging this technology is essential for staying ahead in a competitive and ever-evolving industry.

Features
- 0.56 Inch Digit Height (14.20mm): Provides clear and visible numeric displays, ideal for reading from a moderate distance.
- Dimensions: Compact size of 25.00 x 19.00 mm, suitable for applications where space efficiency is important.
- Low Current Operation: Energy-efficient design, beneficial for reducing power consumption, especially in battery-powered devices.
- Common Anode and Common Cathode Availability: Offers design flexibility to accommodate different types of electronic circuits.
- Excellent Character Appearance: Ensures sharp and clear numeric visibility, crucial for readability.
- High Light Output: Bright display ensures visibility under various lighting conditions.
- Easy Mounting on PC Boards or Sockets: Simplifies the process of integration onto printed circuit boards or into sockets, facilitating ease of use in assembly.
- IC Compatible: Can be easily interfaced with various integrated circuits, making it suitable for complex electronic designs.
- Multicolor Availability: Comes in different colors, offering options for customization and various design requirements.
- Categorized for Luminous Intensity: Ensures consistent brightness across units for uniform appearance and performance.
- Technically Rugged: Durable and reliable, built to withstand various operational conditions and environments.
- Standard Design: Features a gray surface with white segments for a classic, clear display appearance.
- RoHS Compliance: Manufactured in compliance with environmental and health safety standards.
Applications
- Digital Clocks and Timers: Ideal for timekeeping devices in various settings, including schools, offices, and public areas.
- Electronic Scoreboards: Suitable for sports arenas and event venues for displaying scores, times, or other numerical information.
- Industrial Equipment: Used in machinery for displaying measurements, counts, or operational data.
- Consumer Electronics: Incorporated in appliances like microwave ovens, washing machines, and audio equipment for setting displays.
- Medical Devices: Employed in medical equipment for showing readings, timers, and other numerical data.
- Automotive Displays: Useful for displaying information in car dashboards, such as temperature, fuel level, or other indicators.
- Control Panels: Applicable in control panels for machinery, HVAC systems, and other industrial systems.
- Telecommunication Equipment: Used in network devices for displaying channel numbers or signal strength.
Electrical-optical characteristics:
Part No. (Cathode) | Part No. (Anode) | Emitting Color | Material | Peak Wavelength (nm) | Voltage typ.(v) | Voltage max. (v) | Luminous min | Luminous typ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BL-D56C-23B |
BL-D56D-23B |
ultra Blue |
InGaN/SiC |
470 |
4.2 |
35 |
50 |
|
BL-D56C-23D |
BL-D56D-23D |
Super Red |
GaAlAs/DH |
660 |
2.2 |
100 |
140 |
|
BL-D56C-23E |
BL-D56D-23E |
Orange |
GaAsP/GaP |
635 |
2.5 |
40 |
60 |
|
BL-D56C-23G |
BL-D56D-23G |
Green |
GaP/GaP |
570 |
2.5 |
35 |
55 |
|
BL-D56C-23H |
BL-D56D-23H |
Red |
GaP/GaP |
700 |
2.6 |
8 |
12 |
|
BL-D56C-23PG |
BL-D56D-23PG |
Ultra Pure Green |
InGaN/SiC |
525 |
4.2 |
120 |
190 |
|
BL-D56C-23S |
BL-D56D-23S |
Hi Red |
GaAlAs/SH |
660 |
2.2 |
80 |
120 |
|
BL-D56C-23UB |
BL-D56D-23UB |
ultra Blue |
InGaN/SiC |
470 |
4.2 |
60 |
88 |
|
BL-D56C-23UE |
BL-D56D-23UE |
Ultra Orange |
AlGaInP |
630 |
2.5 |
75 |
120 |
|
BL-D56C-23UG |
BL-D56D-23UG |
Ultra Green |
AlGaInP |
574 |
2.5 |
50 |
75 |
|
BL-D56C-23UR |
BL-D56D-23UR |
Ultra Red |
GaAlAs/DDH |
660 |
2.2 |
105 |
160 |
|
BL-D56C-23UY |
BL-D56D-23UY |
Ultra Yellow |
AlGaInP |
590 |
2.5 |
50 |
75 |
|
BL-D56C-23W |
BL-D56D-23W |
Ultra White |
InGaN |
- |
4.2 |
88 |
||
BL-D56C-23Y |
BL-D56D-23Y |
Yellow |
GaAsP/GaP |
585 |
2.5 |
40 |
60 |
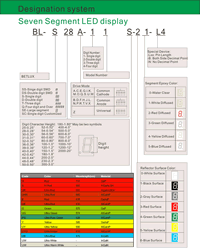
Partno description:
More information
Reflector Surface color (1st number)/ Segment Lens color (2nd number):
| Number | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Ref Surface Color | White | Black | Gray | Red | Green | |
| Epoxy Color | Water clear | White diffused | Red Diffused | Green Diffused | Yellow Diffused |
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta= 25°C)
| Parameter | S | D | UR | E | Y | G | Unit | |
| Forward Current IF | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 30 | mA | |
| Power Dissipation Pd | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 65 | mW | |
| Reverse Voltage VR | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | V | |
| Peak Forward Current IPF (Duty 1/10 @1KHZ) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | mA | |
| Operation Temperature TOPR | -40 to +80 | °C | ||||||
| Storage Temperature TSTG | -40 to +85 | °C | ||||||
| Lead Soldering Temperature TSOL | Max.260+ 5°C for 3 sec Max. ( 1.6mm from the base of the epoxy bulb) | °C | ||||||
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta= 25°C)
| Parameter | UHR | UE | YO | UY | UG | PG | UB | UW | Unit |
| Forward Current IF | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | mA |
| Power Dissipation Pd | 75 | 65 | 65 | 65 | 75 | 110 | 120 | 120 | mW |
| Reverse Voltage VR | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | V |
| Peak Forward Current IPF (Duty 1/10 @1KHZ) | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 100 | 100 | mA |
| Operation Temperature TOPR | -40 to +80 | °C | |||||||
| Storage Temperature TSTG | -40 to +85 | °C | |||||||
| Lead Soldering Temperature TSOL | Max.260+ 5°C for 3 sec Max. ( 1.6mm from the base of the epoxy bulb) | °C | |||||||
Related Information
Applied for:




1. Application
The Seven Segment LED is widely applied for ordinary electronic equipment (such as office equipment,
communication equipment and household applications). Checking with BETLUX’s Sales in
advance for information on applications in which exceptional reliability is required, particularly
when the failure or malfunction of the LEDs may directly jeopardize life or health (such as in
aviation, transportation, traffic control equipment, medical and life support systems and safety
devices).
2. Storage
The storage ambient for the Seven Segment LED should not exceed 30℃ temperature or 70% relative humidity.
For extended storage out of their original packaging, it is recommended that the Seven Segment LEDs be stored
in a sealed container with appropriate desiccant, or in a desiccator with nitrogen ambient.
3. Cleaning
Avoid using any unspecified chemical solvent to clean LED . For example, Trichloroethylene, Chlorosen, Acetone, and Diflon S3MC.
Any cleaning method can only be taken under normal temperature in one minute or less if it is required.
Use water to clean the Seven Segment LED if necessary under room temperature
dry it immediately after that.
4.Forming
Any unsuitable stress applied to the epoxy may break bonding wires in LED
Any forming on lead pin must be done before soldering, not during or after soldering.
Avoid applying any stress to resin in order to prevent the epoxy fracture and break on bonding wire.
While forming, please use a tie bar cut or equivalent to hold or bend the pin.
2mm from the base of resin is the minimum distance for the place bending the lead pin.
Avoid bending the lead pin at the same point twice or more.
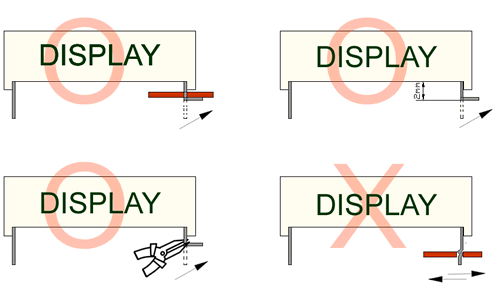
Soldering
When soldering, leave a minimum of 2mm clearance from the base of the base of the lens to the soldering point. Dipping the lens into the solder must be avoided.
Do not apply any external stress to the lead frame during soldering while the LED is at high temperature.
Recommended soldering conditions:
| IR Reflow Soldering (for SMD display) | Wave Soldering | Soldering Iron | |||
| Pre-Heat | 150-180°C | Pre-Heat | 100°C Max. | Temperature | 300°C Max. |
| Pre-Heat Time | 120sec Max. | Pre-Heat Time | 60sec Max. | ||
| Peak Temperature | 260°C Max. | SolderWave | 260°C Max. | Soldering Time | 3sec Max.(one time only) |
| Soldering Time | 10 sec Max. | Soldering Time | 5sec Max. | ||
Note: Excessive soldering temperature and/or time might result in deformation of the LED lens or failure of the LED
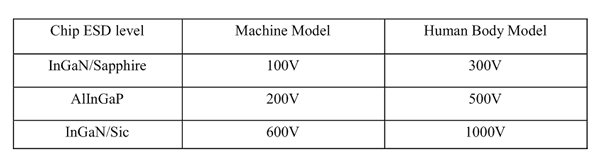
ESD(Electrostatic Discharge)
Static Electricity or power surge will damage the LED.
Suggestions to prevent ESD (Electrostatic Discharge):
n Use a conductive wrist band or anti-electrostatic glove when handling these LEDs
n All devices, equipment, and machinery must be properly grounded
n Work tables, storage racks, etc. should be properly grounded
n Use ion blower to neutralize the static charge which might have built up on surface of the LED’s
plastic lens as a result of friction between LEDs during storage and handling
ESD-damaged LEDs will exhibit abnormal characteristics such as high reverse leakage current,
low forward voltage, or “no light on” at low currents. To verify for ESD damage, check for “light on”
and Vf of the suspect LEDs at low currents.
The Vf of “good” LEDs should be>2.0V@0.1mA for InGaN product and >1.4V@0.1mA for AlInGaP
product.
LED dirve IC by Maxim Integrated
MAX6959 4½-Digit LED Display Driver
MAX6958 4½-Digit LED Display Driver
MAX6955 7-, 14-, 16-Segment LED Display Driver
MAX6956 LED Static Display Driver and I/O Port
MAX6954 7-, 14-, 16-Segment LED Display Driver
MAX6952 5 x 7 Matrix LED Display Driver
MAX6957 LED Static Display Driver and I/O Port
MAX6950 5-Digit LED Display Driver
MAX6951 8-Digit LED Display Driver
ICM7212 4-Digit LED Driver
ICM7212A 4-Digit LED Driver
ICM7212AM 4-Digit LED Driver
ICM7212M 4-Digit LED Driver
ICM7218A 8-Digit LED Driver
ICM7218B 8-Digit LED Driver
ICM7218C 8-Digit LED Driver
ICM7218D 8-Digit LED Driver
MAX7221 8-Digit LED Display Driver
MAX7219 8-Digit LED Display Driver
When selecting power for LED systems, it’s essential to understand several key parameters to ensure safe operation, longevity, and optimal performance. Here are some steps and considerations for LED power selection:
- Determine the Forward Voltage (Vf) of the LED(s):
Each LED has a forward voltage, which is the voltage at which the LED operates when the current is flowing through it. This value can typically be found in the LED’s datasheet.
- Determine the Forward Current (If) of the LED(s):
The forward current is the current at which the LED is designed to operate. Running an LED at higher than its rated current can reduce its lifespan and increase the heat it produces.
- Decide on the Configuration:
Series Configuration: When LEDs are connected in series, the forward voltages add up, but the current remains the same.
Parallel Configuration: When LEDs are connected in parallel, the forward voltage remains the same, but the currents add up. This configuration can be risky because if one LED fails or has a slightly lower forward voltage, it can cause the other LEDs to draw more current.
Calculate Total Power Requirements:
Power (W) = Total Forward Voltage (V) x Total Forward Current (A)
For example, if you have three LEDs connected in series, each with a forward voltage of 3V and a forward current of 20mA, the total power requirement would be:
Power = (3V + 3V + 3V) x 20mA = 9V x 0.02A = 0.18W
- Select an Appropriate Power Supply:
- Voltage Rating: The power supply voltage should match or slightly exceed the total forward voltage of your LED configuration.
- Current Rating: The power supply’s current rating should meet or exceed the total forward current of your LED configuration.
- Safety Margin: It’s a good practice to select a power supply that can provide at least 20% more power than your calculated requirement. This ensures the power supply isn’t operating at its maximum capacity, which can extend its life and ensure safer operation.
- Consider Additional Features:
- Dimming Capability: If you want to control the brightness of your LEDs, choose a power supply with dimming capabilities.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: To protect your LEDs, select a power supply with built-in protection mechanisms.
- Thermal Management: Ensure that the power supply has adequate cooling, especially if it will be enclosed or in a location with limited airflow.
- Regulation and Efficiency:A power supply with good regulation will maintain a consistent voltage output despite variations in the load. High efficiency ensures minimal power is wasted as heat.
- Physical Size and Form Factor:Depending on where you plan to place the power supply, its size and shape may be critical factors.
In summary, when selecting power for LED systems, understanding your LED’s requirements and the configuration you plan to use is essential. Then, pick a power supply that meets those needs with some added safety margin, keeping in mind any additional features or constraints relevant to your project.
Here are some well-regarded brands in the industry:
- Mean Well: One of the most recognized brands in the LED power supply industry, Mean Well offers a wide range of products suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Their units often come with features like overcurrent protection, dimming capabilities, and high efficiency.
- Tridonic: A global leader in lighting technology, Tridonic offers LED drivers and power supplies that cater to various lighting solutions, from simple setups to advanced smart lighting systems.
- Philips Advance Xitanium: Philips is a well-known brand in the lighting industry, and their Xitanium series of LED drivers are known for reliability and performance. They cater to both indoor and outdoor LED applications.
- Osram: Another giant in the lighting industry, Osram offers a range of LED drivers and power supplies suitable for various applications, including architectural and street lighting.
- LIFUD: Specializing in LED drivers, LIFUD is known for its high-quality products that cater to both commercial and residential LED lighting solutions.
- MOSO: This brand offers a variety of LED drivers, especially for outdoor and industrial applications. Their products are known for durability and performance.
- TDK-Lambda: With a history in power electronics, TDK-Lambda offers a range of power supplies and LED drivers suitable for various applications, emphasizing reliability and advanced features.
Need help?
No related products found.